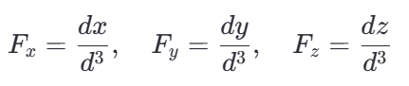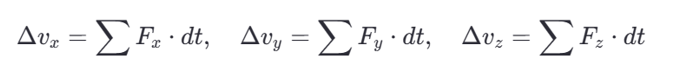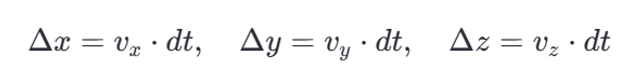1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
| #include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "timer.h"
#include "check.h"
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#define SOFTENING 1e-9f
#define BLOCK_SIZE 128
#define BLOCK_STEP 32
/*
* Each body contains x, y, and z coordinate positions,
* as well as velocities in the x, y, and z directions.
*/
typedef struct
{
float x, y, z, vx, vy, vz;
} Body;
/*
* Do not modify this function. A constraint of this exercise is
* that it remain a host function.
*/
void randomizeBodies(float *data, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
data[i] = 2.0f * (rand() / (float)RAND_MAX) - 1.0f;
}
}
/*
* This function calculates the gravitational impact of all bodies in the system
* on all others, but does not update their positions.
*/
__global__ void bodyForce(Body *p, float dt, int n)
{
// 从全局内存获取本线程负责的物体。
int i = (threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x) % n;
Body body = p[i];
// 块级共享内存,用于缓存一个批次的施力物体。
__shared__ float3 tile[BLOCK_SIZE];
float Fx = 0.0f;
float Fy = 0.0f;
float Fz = 0.0f;
int nBlocks = n / BLOCK_SIZE;
int k = blockIdx.x + blockIdx.x / nBlocks;
#pragma unroll 32
for (int swap = 0; swap < n / (BLOCK_STEP * BLOCK_SIZE); swap++)
{
k %= nBlocks;
// 从全局内存获取新一批物体,装入共享内存。
Body temp = p[k * BLOCK_SIZE + threadIdx.x];
tile[threadIdx.x] = make_float3(temp.x, temp.y, temp.z);
// 确保新一批物体已经全部装入。
__syncthreads();
#pragma unroll 32
// 叠加新一批物体施加在负责物体上的引力。
for (int j = 0; j < BLOCK_SIZE; j++)
{
float dx = tile[j].x - body.x;
float dy = tile[j].y - body.y;
float dz = tile[j].z - body.z;
float distSqr = dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz + SOFTENING;
float invDist = rsqrtf(distSqr);
float invDist3 = invDist * invDist * invDist;
Fx += dx * invDist3;
Fy += dy * invDist3;
Fz += dz * invDist3;
}
// 确保新一批物体已经全部消耗。
__syncthreads();
k += BLOCK_STEP;
}
// 使用原子加法更新速度,避免竞态问题。
atomicAdd(&p[i].vx, dt * Fx);
atomicAdd(&p[i].vy, dt * Fy);
atomicAdd(&p[i].vz, dt * Fz);
}
__global__ void integratePosition(Body *p, float dt, int n)
{
// 计算本线程负责的物体的下标。
int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
if (i >= n)
{
return;
}
// 更新坐标。
p[i].x += p[i].vx * dt;
p[i].y += p[i].vy * dt;
p[i].z += p[i].vz * dt;
}
int main(const int argc, const char **argv)
{
/*
* Do not change the value for `nBodies` here. If you would like to modify it,
* pass values into the command line.
*/
int nBodies = 2 << 11;
int salt = 0;
if (argc > 1)
nBodies = 2 << atoi(argv[1]);
/*
* This salt is for assessment reasons. Tampering with it will result in automatic failure.
*/
if (argc > 2)
salt = atoi(argv[2]);
const float dt = 0.01f; // time step
const int nIters = 10; // simulation iterations
int bytes = nBodies * sizeof(Body);
float *buf;
cudaMallocHost(&buf, bytes);
/*
* As a constraint of this exercise, `randomizeBodies` must remain a host function.
*/
randomizeBodies(buf, 6 * nBodies); // Init pos / vel data
float *d_buf;
cudaMalloc(&d_buf, bytes);
Body *d_p = (Body *)d_buf;
cudaMemcpy(d_buf, buf, bytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
int nBlocks = nBodies / BLOCK_SIZE;
double totalTime = 0.0;
/*
* This simulation will run for 10 cycles of time, calculating gravitational
* interaction amongst bodies, and adjusting their positions to reflect.
*/
/*******************************************************************/
// Do not modify these 2 lines of code.
for (int iter = 0; iter < nIters; iter++)
{
StartTimer();
/*******************************************************************/
/*
* You will likely wish to refactor the work being done in `bodyForce`,
* as well as the work to integrate the positions.
*/
bodyForce<<<nBlocks * BLOCK_STEP, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(d_p, dt, nBodies); // compute interbody forces
/*
* This position integration cannot occur until this round of `bodyForce` has completed.
* Also, the next round of `bodyForce` cannot begin until the integration is complete.
*/
integratePosition<<<nBlocks, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(d_p, dt, nBodies);
if (iter == nIters - 1)
{
cudaMemcpy(buf, d_buf, bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
}
/*******************************************************************/
// Do not modify the code in this section.
const double tElapsed = GetTimer() / 1000.0;
totalTime += tElapsed;
}
double avgTime = totalTime / (double)(nIters);
float billionsOfOpsPerSecond = 1e-9 * nBodies * nBodies / avgTime;
#ifdef ASSESS
checkPerformance(buf, billionsOfOpsPerSecond, salt);
#else
checkAccuracy(buf, nBodies);
printf("%d Bodies: average %0.3f Billion Interactions / second\n", nBodies, billionsOfOpsPerSecond);
salt += 1;
#endif
/*******************************************************************/
/*
* Feel free to modify code below.
*/
cudaFree(d_buf);
cudaFreeHost(buf);
}
|